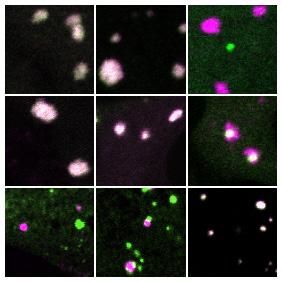
Networks are at the heart of everything from communications systems to pandemics. Now researchers have found that a unique type of network also underlies the structures of critical cellular compartments known as membraneless organelles. These findings may provide key insights into the role of these structures in both disease and cellular operations.
“Prior to this study, we knew the basic physical principle by which these protein-rich compartments form — they condense from the cytoplasm into liquid droplets like dew on a blade of grass,” said David Sanders, a post-doctoral researcher in Chemical and Biological Engineering at Princeton University. “But unlike dew drops, which are composed of a single component (water), cellular droplets are intimidatingly complex. Our work uncovers surprisingly simple principles that we think are universal to the assembly of liquid organelles, and opens new frontiers into studying their role in health and disease.”
Sanders is the lead author in an article in the journal Cell describing a blueprint for the assembly of these liquid structures, also called condensates. The researchers looked closely at two types of condensates, stress granules and processing bodies (“P-bodies”). In the Cell paper, researchers directed by Clifford Brangwynne, a professor of Chemical and Biological Engineering at Princeton and the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, combined genetic engineering and live cell microscopy approaches to reveal the rules underlying the assembly and structure of stress granules, and why they remain distinct from their close relatives, P-bodies.