If it wins FDA approval next year, the two-part sensor could help spot new infections weeks before symptoms begin to show.
Why are pandemics so hard to stop? Often it’s because the disease moves faster than people can be tested for it. The Defense Department is helping to fund a new study to determine whether an under-the-skin biosensor can help trackers keep up — by detecting flu-like infections even before their symptoms begin to show. Its maker, Profusa, says the sensor is on track to try for FDA approval by early next year.
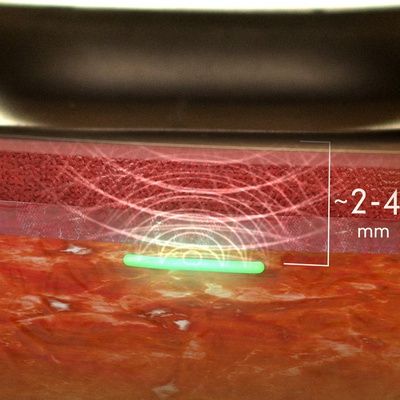
The sensor has two parts. One is a 3mm string of hydrogel, a material whose network of polymer chains is used in some contact lenses and other implants. Inserted under the skin with a syringe, the string includes a specially engineered molecule that sends a fluorescent signal outside of the body when the body begins to fight an infection. The other part is an electronic component attached to the skin. It sends light through the skin, detects the fluorescent signal and generates another signal that the wearer can send to a doctor, website, etc. It’s like a blood lab on the skin that can pick up the body’s response to illness before the presence of other symptoms, like coughing.