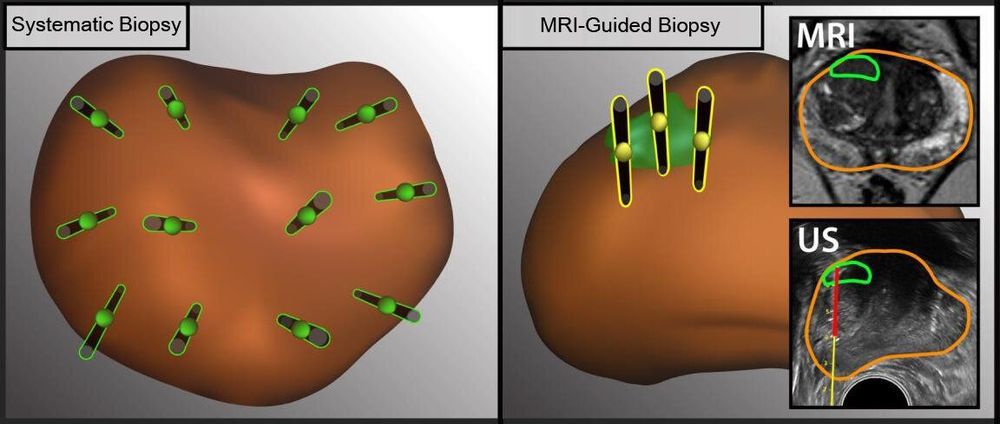
Each year, 1 million men in the U.S. undergo biopsies to determine whether they have prostate cancer. The biopsy procedure traditionally has been guided by ultrasound imaging, but this method cannot clearly display the location of tumors in the prostate gland.
A multidisciplinary team of UCLA physicians has found that a new method, which includes biopsy guided by magnetic resonance imaging, or MRI, can be used together with the traditional method to increase the rate of prostate cancer detection.
Ultrasound has been used to visualize the prostate in order to take a representative sampling of tissue to biopsy. The introduction of MRI has allowed doctors to see specific lesions in the prostate and only take tissue samples from those spots. But the two sampling methods often aren’t used in combination.