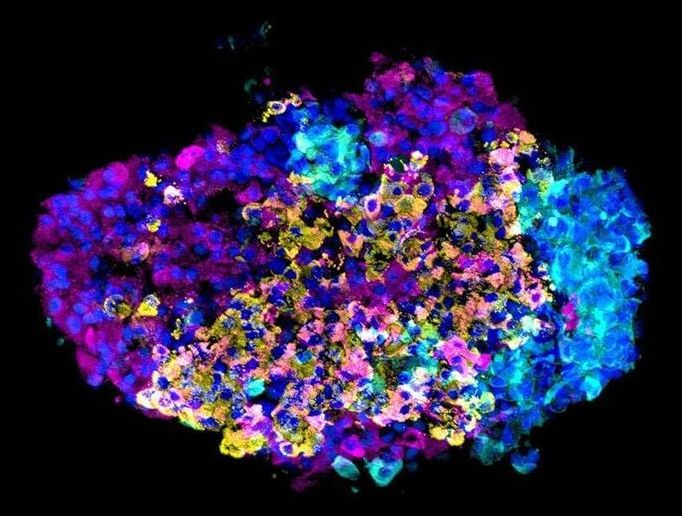
A team of researchers led by Harvard University scientists has improved the laboratory process of converting stem cells into insulin-producing beta cells, using biological and physical separation methods to enrich the proportion of beta cells in a sample. Their findings, published in the journal Nature, may be used to improve beta cell transplants for patients with type 1 diabetes.
In 2014, Douglas Melton’s lab showed for the first time that stem cells could be converted to functional beta cells, taking a step toward giving patients their own source of insulin. In that initial process, beta cells made up 30 percent of the final cell mixture.
“To improve from 30 percent, we needed to really understand the other 70 percent of the resulting cells,” said Adrian Veres, a graduate student in the Melton lab and lead author of the current study. “Until recently, we couldn’t take a sample of our cells and ask what cell types were in there. Now, with the revolution in single-cell sequencing, we can go from nothing to the full list.”