JBEI researchers develop efficient and affordable method for plant DNA assembly.
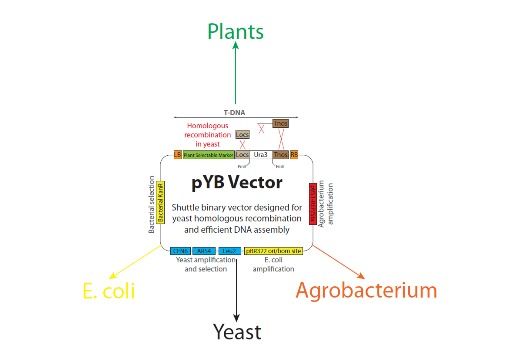
Researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)’s Joint BioEnergy Institute (JBEI) in collaboration with Berkeley Lab’s Environmental Genomics & Systems Biology Division and the DOE Joint Genome Institute developed a versatile system (named jStack) which utilizes yeast homologous recombination to efficiently assemble DNA into plant transformation vectors. The new approach will impact plant engineering for the bioenergy, agricultural and pharmaceutical industries.
Although synthetic biology has provided solutions to many societal challenges, little research has been devoted to advancing synthetic biology in plants. Microbes, such as yeast and Escherichia coli (E. coli), have received much of the attention in developing synthetic biology tools due to their fast generation time and the ease of working with these organisms in laboratories. A shortage of characterized DNA parts, along with the difficulty of efficiently assembling multiple and large fragments of DNA into plant transformation vectors, has limited progress in studying and engineering plants to the same degree as their microbial counterparts.