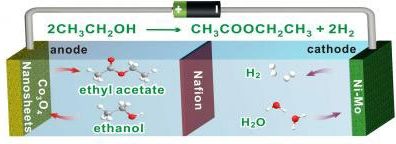
Hydrogen is widely regarded as a promising and clean alternative energy source. The traditional source of hydrogen (H2) for fuel cell use is water, which is split into H2 and oxygen (O2). But O2 is a low-value product.
So, this week in ACS Central Science (“Electrochemical Partial Reforming of Ethanol into Ethyl Acetate Using Ultrathin Co3O4 Nanosheets as a Highly Selective Anode Catalyst”), researchers report a new approach and a new catalyst that can produce not just hydrogen but also valuable chemicals, including the most common ingredient in nail polish.
Researchers have found a way to make the valuable chemical ethyl acetate while generating H2 gas to power fuel cells. (Image: Nanfeng Zheng)