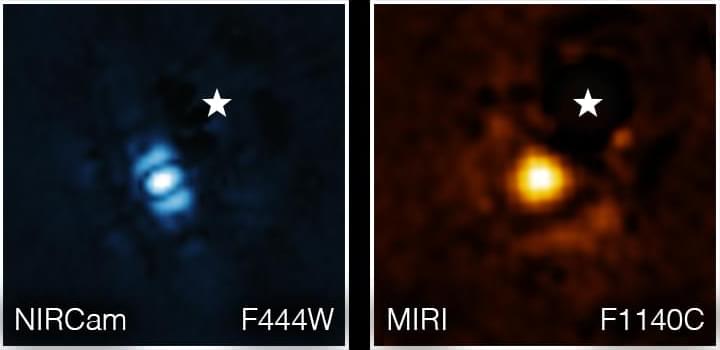
Last week, the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) made the first ever detection of CO2 on an exoplanet. Following that scientific milestone, it has now captured a direct image of another planet – HIP 65,426 b, which orbits the large A-type star HIP 65426. The system is 355 light years from Earth.
Astronomers first discovered this gas giant in July 2017, using the Spectro-Polarimetric High-Contrast Exoplanet Research (SPHERE) instrument belonging to the European Southern Observatory (ESO).
NASA made a follow-up observation to test Webb’s capabilities, using the mid-infrared part of the spectrum to reveal new information that previous telescopes would be unable to detect. The spacecraft’s Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam) and Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI) are both equipped with coronagraphs to block the glare of starlight, which can be 10,000 times brighter than planets. This enables Webb to take direct images of exoplanets.