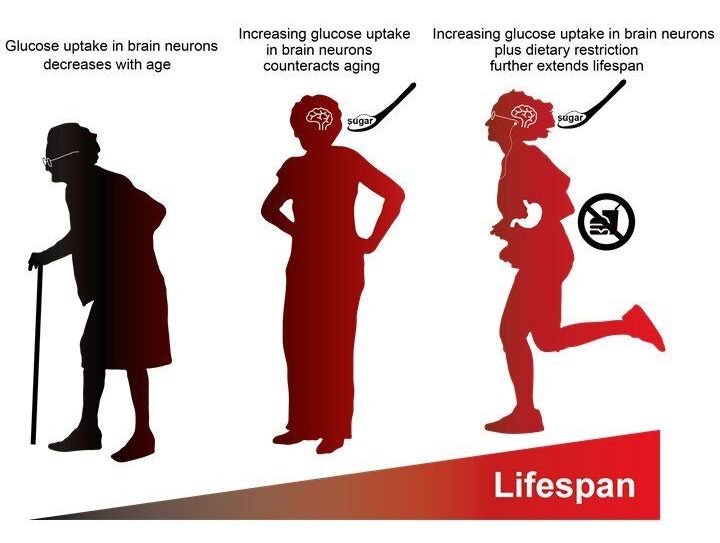
Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have discovered that fruit flies with genetic modifications to enhance glucose uptake have significantly longer lifespans. Looking at the brain cells of aging flies, they found that better glucose uptake compensates for age-related deterioration in motor functions, and led to longer life. The effect was more pronounced when coupled with dietary restrictions. This suggests healthier eating plus improved glucose uptake in the brain might lead to enhanced lifespans.
The brain is a particularly power-hungry part of our bodies, consuming 20% of the oxygen we take in and 25% of the glucose. That’s why it’s so important that it can stay powered, using the glucose to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the “energy courier” of the body. This chemical process, known as glycolysis, happens in both the intracellular fluid and a part of cells known as the mitochondria. But as we get older, our brain cells become less adept at making ATP, something that broadly correlates with less glucose availability. That might suggest that more food for more glucose might actually be a good thing. On the other hand, it is known that a healthier diet actually leads to longer life. Unraveling the mystery surrounding these two contradictory pieces of knowledge might lead to a better understanding of healthier, longer lifespans.
A team led by Associate Professor Kanae Ando studied this problem using Drosophila fruit flies. Firstly, they confirmed that brain cells in older flies tended to have lower levels of ATP, and lower uptake of glucose. They specifically tied this down to lower amounts of the enzymes needed for glycolysis. To counteract this effect, they genetically modified flies to produce more of a glucose-transporting protein called hGut3. Amazingly, this increase in glucose uptake was all that was required to significantly improve the amount of ATP in cells. More specifically, they found that more hGut3 led to less decrease in the production of the enzymes, counteracting the decline with age. Though this did not lead to an improvement in age-related damage to mitochondria, they also suffered less deterioration in locomotor functions.